Chenn Perspective | AI IoT wave of air compressor (above)
Release time:
2023-04-13
In 1950, Alan Turing, the father of computer science, threw out a question to the academic community, "Can machines think?" In this test, if a person asks a question to a person and a machine at the same time. If the person asking the question cannot distinguish whether the answer is a human or a machine, then the machine can "think". This is the Turing Test (Turing Test).

In 1950, Alan Turing, the father of computer science, threw out a question to the academic community, "Can machines think?" In this test, if a person asks a question to a person and a machine at the same time. If the person asking the question cannot distinguish whether the answer is a human or a machine, then the machine can "think". This is the Turing Test (Turing Test).
Chennai View|What is AI?

McCarthy, the 1971 Turing Award winner and father of artificial intelligence, described AI as "a system that can run and think like a human in order to be considered intelligent."

Although artificial intelligence seems to be a major trend now, its development once had a bumpy ride.
Chennai View|Golden Age
In the summer of 1956, Dartmouth College held the first-ever academic symposium on artificial intelligence, which applied for funding from the Rockefeller Foundation, and which read as follows:
"We will try to find how to make machines use language, form abstracted concepts, solve various problems now reserved for humans, and improve themselves. We believe that if a carefully selected group of scientists work together on these problems, significant progress can be made on one or more of them over the course of a summer."
Chennai View|The trough of AI
In the 1970s and 1980s, the development of artificial intelligence was limited and bottlenecked. Due to the limited memory and computing power of computers at the time, AI was unable to solve any real-life problems. Due to the lack of substantial progress, the British and U.S. governments also slowly stopped funding AI research projects. The U.S. National Science Council (NRC) also suspended research funding after funding $20 million.
Chennai View|Second Wave of AI
By the 1980s, the focus of AI research shifted to rule-based prediction systems. Scientists entered all the rules associated with making a decision into a computer, and the computer looked up what predictions it should make based on those rules. For example, suppose a customer entered an order, the computer could predict what other parts this customer would need to work with the parts in the order, which reduced downtime due to missing parts. However, other studies in the 1980s that tried to use similar schemes failed, which indirectly led to a "winter of artificial intelligence" because in most scenarios there were too many exceptions to the "rules" for specific applications.
Chennai View|Real Spring

IBM Supercomputer "Deep Blue" defeated the world chess champion in 1997.
From the 1990s to the present, as technology has exploded in the size of data, computers have become faster and cheaper to process, and there has been a growing bias toward reconstructing problems as prediction problems. This allows algorithms to decide their own "rules", and more data means more exceptions are taken into account in the rules. We also get predictions that are more accurate and more cost effective. And then, with the influx of capital and policy support, the application scenarios of AI are also rapidly increasing, and emerging technologies such as the Internet, cloud computing, big data, and chips are also providing sufficient data support and arithmetic support for the development of AI as well, and what is happening now will have a profound impact on the optimization of social productivity and industrial structure.
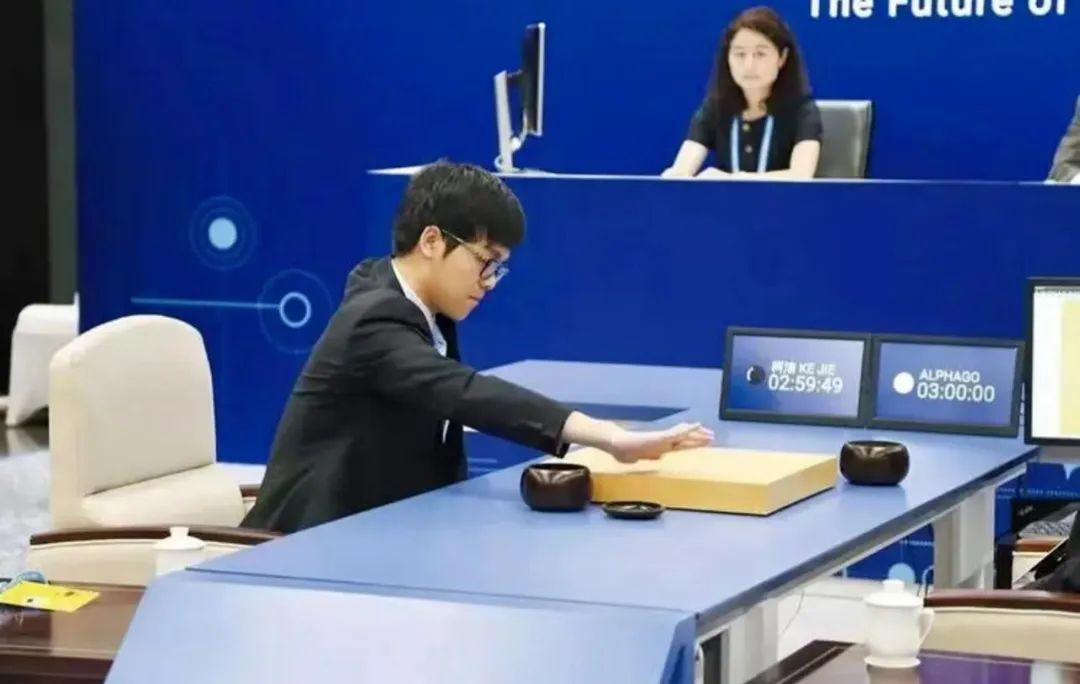

The victory of "Alpha Go" over Ke Jie in 2016
Related news
















